
(Orbit, Tumor, Eyelid Laceration, Enucleation)
Reconstruction involves repair of the orbit and associated structures, including the surrounding skin tissues, tear passages, and bony walls. These can occur from a wide variety of causes, including trauma, nasolacrimal (tear duct) problems, removal of cancer (for example, Mohs' reconstruction after a dermatologist has resected a skin cancer), orbital fracture repair, enucleation (removal of eye) or exenteration (removal of orbit), or other prior surgery.
 |
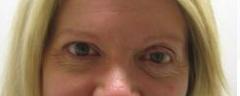 |
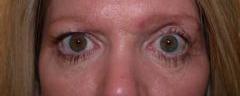
| PREOP: s/p trauma, surgery, and scarring (eyelid retraction) | POSTOP: s/p scar revision, fat implant, and skin graft |
 |
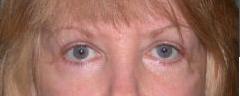 |
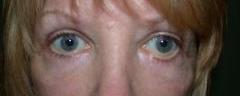
| PREOP: scarring and eyelid refraction from prior surgery | POSTOP: s/p release of scar tissue |
 |
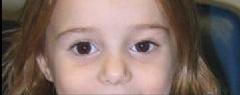 |
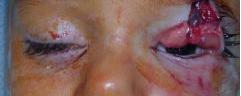
| PREOP: Eyelid laceration, involving nasolacrimal passage (dog bite) | POSTOP: s/p nasolacrimal repair and eyelid repair |
 |
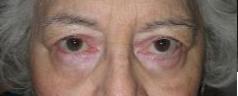 |
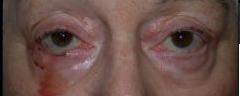
| PREOP: Mohs' excision of eyelid tumor | POSTOP: s/p Mohs's reconstruction |
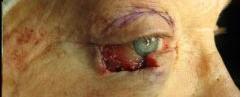 |
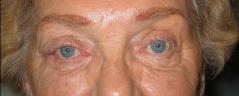 |
| PREOP: Mohs' tumor excision | POSTOP: s/p Mohs' reconstruction |
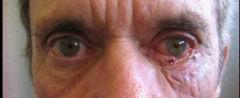 |
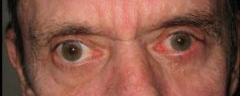 |
| PREOP: Mohs' excision of eyelid tumor | POSTOP: s/p Mohs' reconstruction |
 |
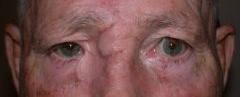 |
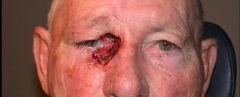
| PREOP: Mohs' excision of tumor involving lid and lacrimal passage | POSTOP: s/p Mohs' reconstruction |
 |
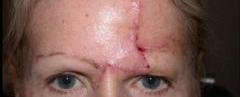 |
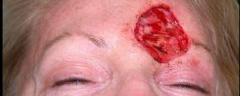
| PREOP: Mohs' resection of tumor | POSTOP: s/p Mohs' reconstruction with free flap |
 |
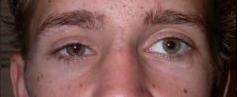 |
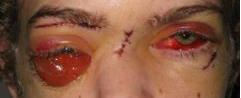
| PREOP: ruptured globe (right eye) after trauma | POSTOP: s/p enucleation (right eye) |







